Greener Coils: Sustainable Materials for Winding Machine Innovation
Introduction: Sustainability in Winding Technology
The need for sustainability in manufacturing has moved from preference to priority. As climate goals tighten and eco-conscious markets expand, the materials used in industrial equipment, including winding machines are under intense scrutiny. Traditionally, machine components were chosen for performance and cost, sometimes at the expense of environmental impact. Today, leading manufacturers are innovating with eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs, recognizing that a greener footprint is essential for both regulatory compliance and brand value.
Eco-Friendly Materials: Beyond the Basics
At the core of this transformation is a systematic rethink of what winding machines are made from. Metals like copper and aluminium, while still important, are now sourced with attention to responsible mining and recycling. Secondary alloys and recycled grades are increasingly chosen for their lower carbon profile and retained mechanical properties. Insulation components and protective layers, historically made from petroleum-based plastics and varnishes, are being replaced with biodegradable, low-VOC, or recycled alternatives to reduce toxic emissions and landfill waste.
Composite innovations are entering the spotlight. Nanomaterial-reinforced structures promise greater durability, lighter weights, and improved thermal management with less environmental impact. Carbon-fibre composites, once a purely performance-driven choice, are now being engineered with bio-based resins or recycled content, merging strength with sustainability. These new material approaches allow winding machines to achieve high speeds and tighter tolerances without adding to environmental burdens.
Sustainability in Coil and Stator Engineering
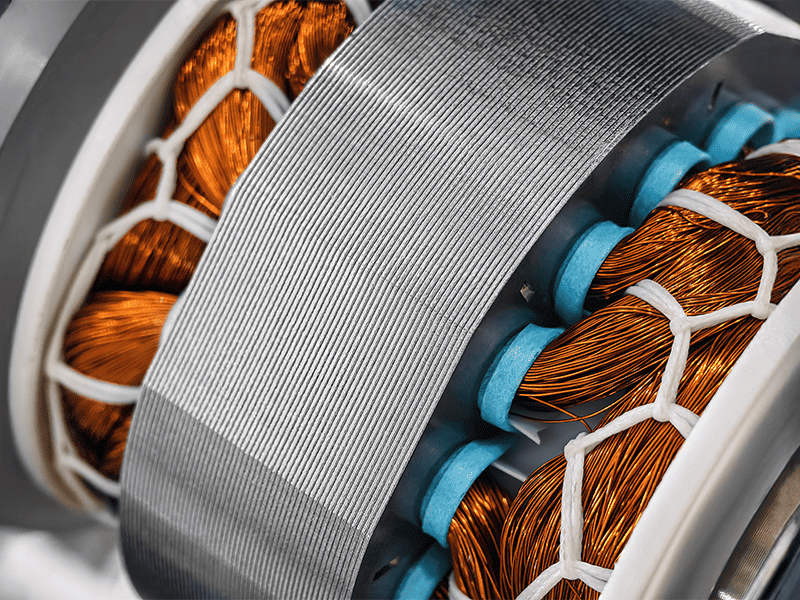
Making winding machines more sustainable isn’t just about their frames and gears; it also impacts every coil, bobbin, and stator produced. Eco-friendly winding processes use recyclable metals and biodegradable insulating tapes. Some innovators have adopted minimalist packaging to further limit waste, intentionally designing components for easy recycling at end-of-life.
Locally sourcing winding materials can dramatically reduce transportation emissions, and advanced automation enables more precise wire use, minimizing scrap. Even evaporative coolants and lubricants are being reformulated as bio-lubricants, cutting hazardous waste. This holistic approach doesn’t only reduce carbon. It ensures the durability and performance of winding machines remain uncompromised.
Innovative Approaches for a Green Future
Innovation in sustainable materials is closely linked to advances in manufacturing technology. Thermoplastic tape winding, for instance, enables the instant consolidation of prepregs during filament winding, eliminating the need for energy-intensive post-processing. This reduces the carbon footprint of composite components and allows more versatile production including complex shapes that might require excess material with traditional methods.
Smart winding machines now track fibre tension, resin temperature, and energy usage in real time, enabling plant managers to optimize sustainability metrics. Integration with IoT and analytics platforms means that sustainability can be measured and improved continuously, not just assessed at purchase. Firms in the EV supply chain leverage these data-driven insights to shrink copper waste and select plant power from renewable sources, turning winding into a driver for clean manufacturing.
Self-healing polymers and shape-memory alloys are on the horizon. Gearboxes and guides that repair minor wear without manual intervention extend machine life, reducing both raw material and maintenance waste. Using shape-memory polymers for adjustable guides with low-energy actuation means simple mechanisms and fewer resource-demanding replacements over time.
Overcoming the “Sustainability vs. Durability” Myth
A common misconception persists that sustainable materials lack the ruggedness needed for industrial applications. Yet recent advancements debunk this myth. Bio-derived composites and recycled metals now match the fatigue strength, impact resistance, and corrosion performance of their traditional counterparts. For electrical insulation, modern biopolymers can outperform petrochemical varieties in moisture resistance, breakdown voltage, and longevity.
Current research into natural fibres as viable alternatives for reinforcement (hemp, flax, jute) shows potential for lighter, more resilient winding machine housings and covers, while keeping carbon emissions low. The rise of these novel materials is rooted in relentless innovation, extensive testing, and growing commercial adoption. Companies embracing this evolution are not only future-proofing their supply chains, but they’re raising the quality bar, proving that sustainability and durability can coexist.
The Roadmap to a Greener Winding Machine Sector
Adopting sustainable materials involves more than selecting new grades or suppliers. It means re-evaluating the full product lifecycle, from design and manufacturing to usage and disposal. Leading winding machine manufacturers apply eco-design principles: minimizing part complexity, optimizing for energy efficiency, and choosing materials that enable end-of-life recycling and recovery. Some plants are transitioning to circular economy models, recapturing scrap metals, packaging, and plastics for remanufacture across multiple product lines.
Collaboration is key to accelerating innovation. Partnerships among machine builders, material scientists, and recycling specialists are yielding breakthrough components. These include components from low-carbon motors and gearboxes to bio-lubricated bearings and biodegradable bobbin carriers. By sharing data, best practices, and pilot results, the industry can push the boundaries of what’s possible, making winding machines both smarter and more sustainable.
Measuring Impact and Value for Stakeholders
The business case for eco-friendly winding machines is expanding. Customers increasingly demand assurances of sustainability in their supply chain, from EV makers to renewable energy manufacturers. Certifications for eco-friendly products and processes are now part of purchasing guidelines, and regulatory incentives reward companies who demonstrate meaningful carbon savings.
Sustainable innovation is also a brand asset. Firms leading in material and environmental stewardship are strengthening their market position, enhancing employee pride, and attracting talent eager to work on impactful projects. Financially, the shift to energy-efficient, durable, and recyclable winding machines reduces operating costs, improves compliance, and opens doors to premium markets. When sustainability is embedded in material choice and manufacturing, value is created for all stakeholders including internal, external, and societal.
Conclusion: Building for a Sustainable Future
The journey to a greener winding machine sector is as much about innovation as it is about responsibility. Small changes in material selection, production methods, and lifecycle thinking aggregate to substantial environmental impact. The most advanced designs now combine eco-friendly composites, recyclable metals, smart automation, and data-driven energy management in one intelligent package. As global industries, regulators, and customers continue demanding sustainable solutions, winding machine manufacturers have an opportunity to shape the future of industrial sustainability itself.
In embracing sustainable materials, the winding machine industry sets new standards for how performance and environmental stewardship intersect. By making each component a little greener and every process a little smarter, manufacturers can lead the next era of progress where innovation, durability, and eco-friendly design go hand in hand.

